Commercial Lease Agreement
Leasing law is biased against the Landlord in Australia. Fight back by getting your Tenant to sign a Legal Consolidated Commercial Lease. This Lease Agreement is suitable for Australian commercial property. It also accommodates:
- where the tenant is acting as trustee of a trust
- guarantors
The law firm’s Commercial Lease:
- provides low-cost dispute resolution
- reduces unconscionable conduct claims and attacks against the Landlord
Commercial lease vs Retail Lease
In Australia, there are two types of leased properties: residential and commercial. Commercial leases are either ‘commercial’ or ‘retail’; each relevant state and territory regulates both.
‘Commercial’ leases are for offices, warehouses and industrial sites. There is little ‘retail’ activity. A ‘commercial’ lease does not require the draconian laws that ‘retail‘ properties suffer. This is because:
- The law sees a balance of power between the landlord and the tenant for commercial leases.
- Whereas, for retail leases, the government believes that the tenant has less power than the landlord.
This is supposedly because ‘retail’ tenants are at the mercy of the big shopping centre owners. Shopping centres control 38% of Australian retail space. There is $45B of shopping centres in the hands of the six biggest owners. They are Westfields, CFX, Federation, AMP, Dexus and Lend Lease. Therefore, in the interest of ‘fairness’, a ‘retail’ landlord’s powers are restricted.
You are building only a Commercial Lease. This is not a Retail Shop Lease. If you need a Retail Shop Lease, telephone us.
Subletting in a commercial lease
A sublease occurs when the tenant rents out all or part of the premises to a third party. Ensure your commercial lease agreement addresses whether subletting is allowed. Many landlords require the tenant to seek written consent before subleasing. This protects the landlord’s interests and maintains control over the use of the premises.
The Tenant has no authority to sublet under this Lease. This is unless the Landlord and Tenant mutually agree. The ‘waive and variation’ clause permits subletting and assignment – but only with the Landlord’s consent.
Landlord protected from Damages
If the Tenant defaults on payment, the landlord recovers the agreed-upon damages. This commercial lease uses a unique formula to calculate damages, which is in accordance with Court cases.
Landlord gains flexibility with waivers
Many lease agreements cannot be updated. However, with our lease, the Landlord and Tenant can agree to vary any of the terms of the Commercial Lease. This suits changing needs over the years. An email exchange can update the lease.
Why a Guarantor in a Commercial Lease?
A Lease agreement is between the landlord and the tenant. Sometimes, a guarantor acts as a third party to provide extra security to the landlord.
A guarantor co-signs the lease agreement with the tenant and assumes the tenant’s financial and other obligations under the lease.
What is a Guarantor?
The guarantor in a Lease agreement adds and signs their name to the contract. The guarantor agrees to pay the rent if the tenant is unable to do so. Specific clauses of the lease outline the responsibilities of the lease guarantor. These include the payment schedule and other responsibilities.
A guarantor stands in the shoes of the tenant. Whatever the tenant fails to do under the lease, the guarantor must now do. The guarantor agrees to guarantee all of the tenant’s obligations under the lease. These obligations include:
- Payment of rent.
- Cost of making good damage to the premises.
- Covering defaults by the tenant.
- Compensating for early termination of the lease.
- Loss suffered by the landlord in reinstating and re-letting the premises.
- Cost of the reduction in rent if the premises are re-let on terms less advantageous to the landlord.
- Legal costs for tenant default.
It is an onerous responsibility.
A Landlord often wants another person to guarantee the tenant’s performance. Perhaps the tenant is a company with no assets.
Landlords often demand a guarantor when the tenant has little income or assets. Perhaps the tenant’s income or credit score is insufficient to secure the desired lease.
What is a Lease Option to Renew?
What is a Lease Option to Renew?
An option agreement grants the tenant the right, but not the obligation, to extend their commercial lease for a further specified term. It provides the tenant with security of tenure, protecting their business location.
If you hear of a ‘5 x 5 x 5’, that refers to a five-year lease with two additional options to extend for a further five years each time. The tenancy could potentially last up to 15 years. Such long business leases are standard where there is valuable site goodwill — for example, a shop on a busy road. Or an accounting firm that has undertaken a $2,000,000 fit-out and does not expect to renovate again for another 15 years.
In contrast, if the location is less important to the tenant, they may only ask for a ‘3 x 3’. This is a three-year lease with the tenant having the option to extend the lease once — for a further three years. This results in a total lease period of six years.
Remember, the landlord is giving away a valuable right. The option to renew the lease has no value to the landlord — quite the opposite. But it has enormous value to the tenant. What if the landlord wants to sell the property? It must be sold subject to the existing tenancy. However, the buyer may have intended to occupy the commercial premises themselves. However, it could be argued that the option gives the tenant ‘peace of mind’ and they are therefore more likely to protect the property and stay longer.
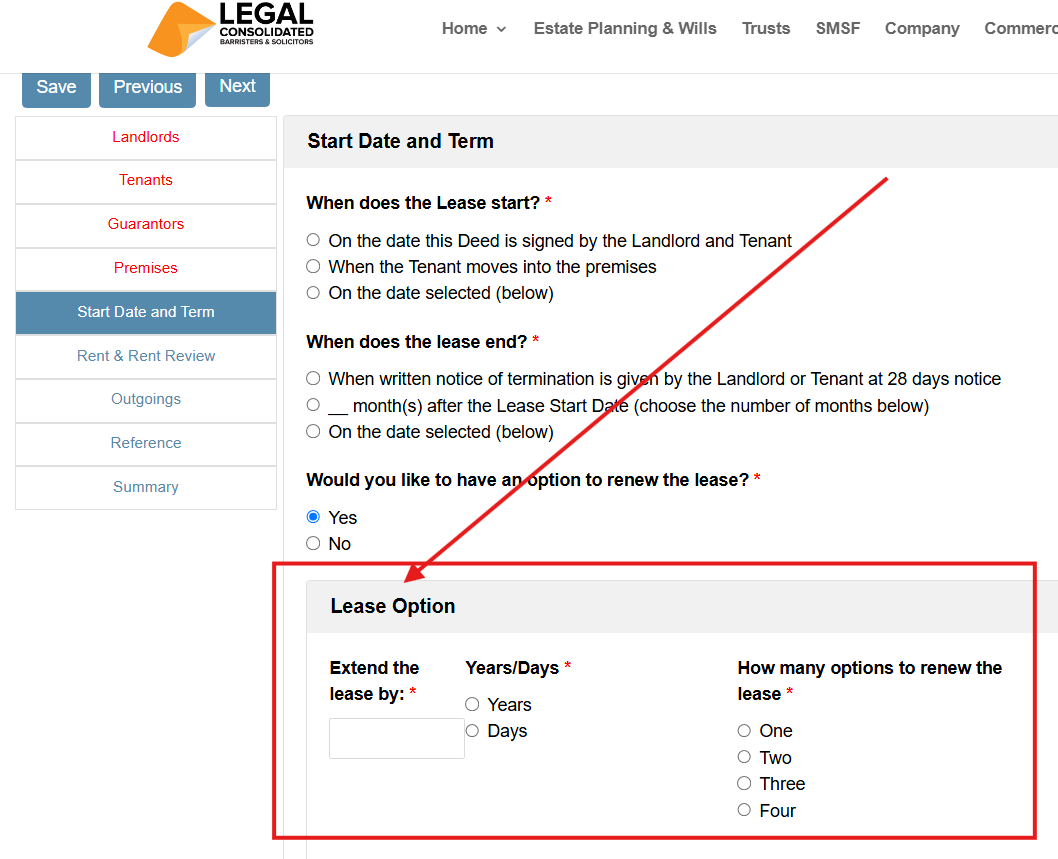
The option is a gift from the Landlord to the Tenant. It allows the Tenant to force the Landlord to extend the Lease for a further number of years.
The Tenant has the privilege of either exercising the option or letting it lapse and leaving.
How to Exercise a Lease Option
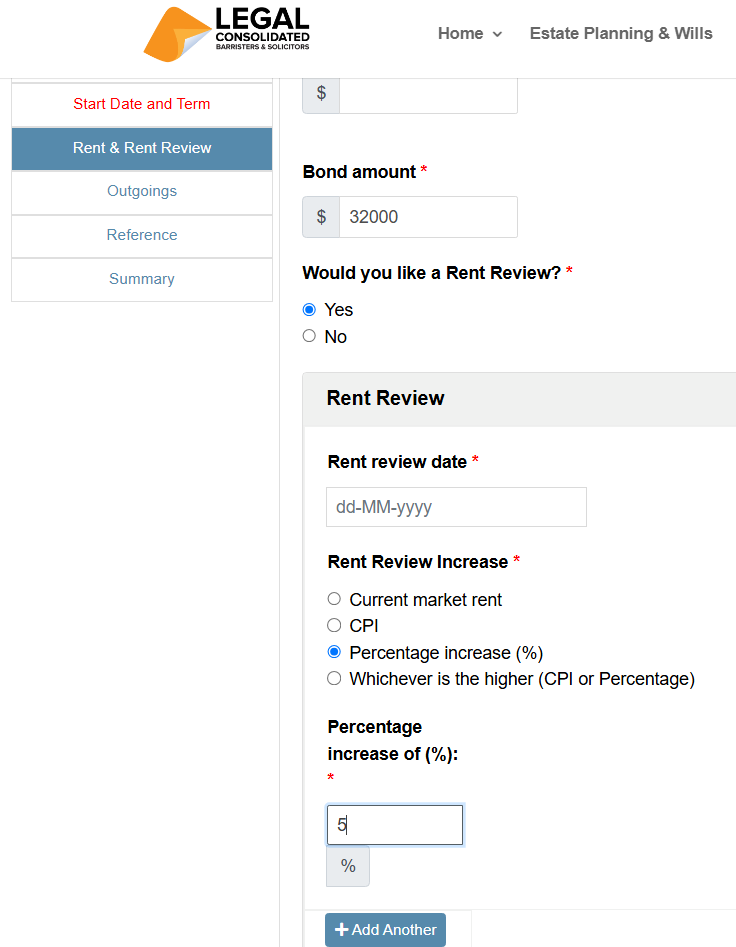
The option is a gift from the Landlord to the Tenant. It allows the Tenant to force the Landlord to extend the Lease for a further number of years.
The Tenant has the privilege of either exercising the option or letting it lapse and leaving.
To exercise the option, the tenant must provide the landlord with formal written notice. This must be done within the strict timeframe stipulated in the lease agreement, typically 3 to 6 months before the current term ends. Missing this deadline forfeits the right to renew.
Benefits of Options for Tenants and Landlords
For the tenant, an option provides valuable business continuity and security. For the landlord, it makes the property more attractive and aids in retaining a reliable tenant. Leases commonly state that the tenant cannot be in breach of the agreement when they exercise the option.
Rent Reviews for Option Periods
The Legal Consolidated lease states how rent for the new term is calculated. This is usually done via:
-
A market rent review;
-
An increase based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI); or
-
A fixed percentage increase.
New Lease vs Exercising a Lease Option
Q: Instead of exercising the option, should I build a new Lease Agreement?
A: Entering into a new lease agreement is always possible, but it requires the consent of both the landlord and the tenant. All terms, including rent and duration, are subject to fresh negotiation, and either party can walk away.
In contrast, an option is a powerful right granted by the landlord to the tenant. It allows the tenant to unilaterally force the landlord to extend the lease for the pre-agreed option term. The landlord cannot refuse if the tenant exercises the option correctly and is not in breach of the lease.
Dealing with Early Termination in a Commercial Lease
Life and business are unpredictable. Both parties benefit from a clearly defined early termination clause. Common elements include:
- Break Fees: Compensation payable to the landlord.
- Notice Periods: Reasonable timeframes for informing the other party. A well-drafted clause balances the interests of both the tenant and the landlord.
Tenant gives Power of Attorney to Landlord
When the lease is over, the Tenant is gone. But what if the Tenant put a caveat on your property? The POA helps remove the caveat and other encumbrances.
Addressing Repairs and Maintenance in a Commercial Lease
Repairs and maintenance clauses often cause disputes. Legal Consolidated clearly states who is responsible for maintaining various parts of the property. For example:
- Structural Repairs: Typically, the landlord’s responsibility.
- Non-Structural Repairs: This usually falls to the tenant. A clear allocation of these duties reduces disagreements and protects the landlord-tenant relationship.
Including a Rent Review Mechanism
Commercial leases often span multiple years. We allow you to include a rent review clause to ensure the rent remains aligned with market conditions, including:
- CPI Adjustments: Linking rent to inflation.
- Market Reviews: Adjusting rent based on prevailing rates in the area.
You can have as many rent review clauses as the landlord wishes. You can add them as you build the commercial lease. However, there is a question of commerciality. The higher the rent, the smaller the pool of tenants you attract, and tenants are more likely to leave at the end of the lease.
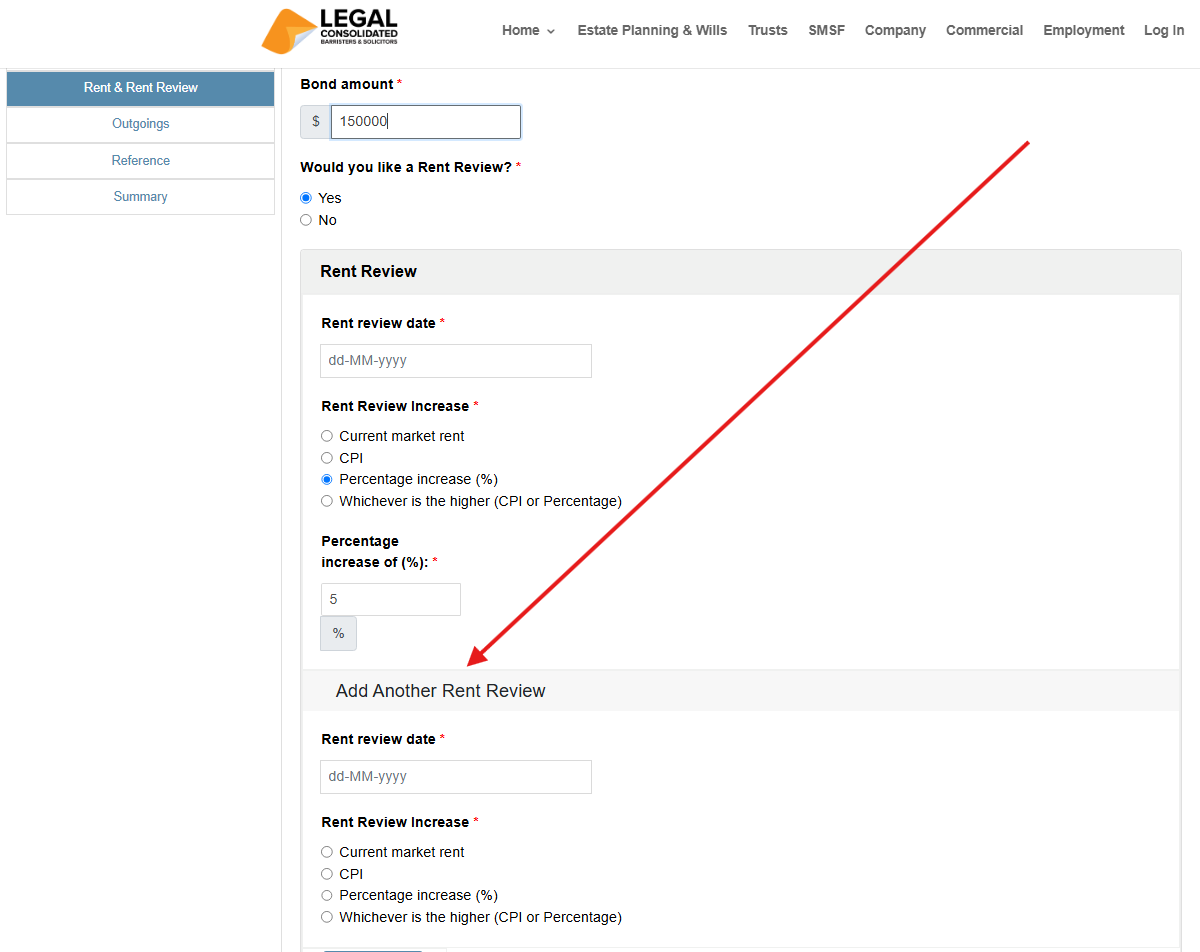
The landlord can add as many rent reviews as they wish. You can conduct a rent review annually or every few years.
Just keep pressing “Add Another Rent Review” as you build the lease.
The Importance of Permitted Use Clauses in Commercial Leases
The permitted use clause defines the tenant’s activities on the premises. For example, a retail store may not operate as a café without explicit permission. Landlords must ensure the permitted use aligns with zoning regulations, while tenants need flexibility for their business operations.
Self-Managed Super Fund leasing commercial property?
What is the sole purpose of your Self-Managed Superannuation Funds (SMSF)? By law, your SMSF only benefits retired members. Take care that a member does not accidentally benefit from the SMSF. There are special issues when an SMSF owns and rents out commercial property to a ‘related party’.
The SMSF rules are stricter when your SMSF leases a commercial property to a member, including the member’s family and business.
Our Commercial Lease complies with the Superannuation law, including:
- a compliant written lease agreement
- an arm’s length transaction – the trustee cannot give ‘special treatment’ to a related party through a lease for commercial property. E.g. rent is at a market rate etc…
- the requirement for duly paid rent, according to the terms of the Commercial Lease
- the trustee takes appropriate action to remedy breaches
- evidence for the SMSF auditor and ATO that it confers no member advantage
Business Structures that can use a Commercial Lease
Family trust
- Family Trust Deed – watch the free training course
- Family Trust Updates:
- Everything – Appointor, Trustee & Deed Update
- Deed ONLY – only update the Deed for tax
- Guardian and Appointor – only update the Guardian & Appointor
- Change the Trustee – change human Trustees and Company Trustees
- The company as Trustee of Family Trust – only for assets protection?
- Bucket Company for Family Trust – tax advantages of a corporate beneficiary
Unit trust
- Unit Trust
- Unit Trust Vesting Deed – wind up your Unit Trust
- Change Unit Trust Trustee – replace the trustee of your Unit Trust
- Company as Trustee of Unit Trust – how to build a company designed to be a trustee of a Unit Trust
Corporate structures
- Partnership Agreement – but what about joint liability?
- Incorporate an Australian Company – best practice with the Constitution
- Upgrade the old Company Constitution – this is why
- Replace lost Company Constitution – about to get an ATO Audit?
Service trust and Independent Contractors Agreements
- Independent Contractor Agreement – make sure the person is NOT an employee
- Service Trust Agreement – operate a second business to move income and wealth
- Law firm Service Trust Agreement – how a law firm runs the backend of its practice
- Medical Doctor Service Trust Agreement – complies with all State rules, including New South Wales
- Dentist Service Trust Agreement – how dentists move income to their family
- Engineering Service Trust Agreement – commonly engineers set up the wrong structure
- Accountants Service Trust Agreement – complies with ATO’s new view on the Phillips case

